OVERVIEW
A generator set is a complete mechanical device that converts other forms of energy into electrical energy. It consists of a power system, control system, silencing system, vibration isolation system, and exhaust system. It is driven by a water turbine, steam turbine, diesel engine, or other power machinery to convert the energy generated from water flow, air flow, fuel combustion, or nuclear fission into mechanical energy transmitted to the generator. The generator then converts this mechanical energy into electrical energy, which is output to be used by electrical equipment. Generators have wide applications in industrial and agricultural production, defense, technology, and daily life. In recent years, with technological advancements, lightweight and portable small generator sets have also become a preferred choice for household emergency power and outdoor activities, entering into the daily lives of residents.
A diesel generator set is an energy conversion device that transforms chemical energy into heat energy, then into mechanical energy, and finally converts it into the required electrical energy. Fuel is its raw material, and electrical energy is its product.
A diesel generator set is an integrated electromechanical device composed of three main components: a diesel engine, an AC generator, and a control system. Its technology encompasses various fields, including mechanical dynamics, electrical engineering, and automation control.
A diesel generator set is a complete system composed of various independent components, and the quality and performance of these individual components have a significant impact on the overall system's quality.
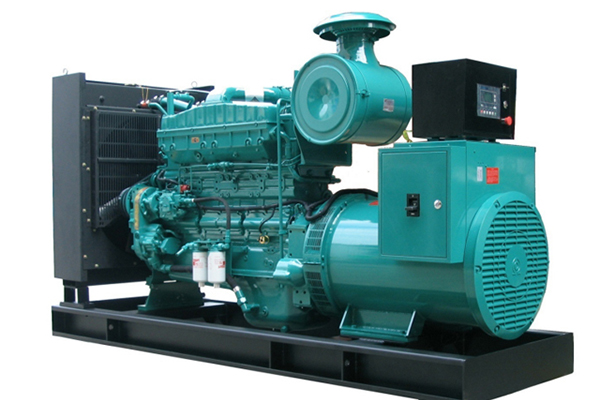
A diesel generator set consists of an engine, a generator, a control system, and various accessories. A typical diesel generator set should have three nameplates: one for the entire unit, one for the engine, and one for the generator. Common diesel generator set manufacturers include Cummins, Simpson, Wilson, Kohler, Caterpillar, and others.
ADVANTAGES
-
Fuel Efficiency: Diesel engines are known for their high thermal efficiency and fuel economy, which means they can generate a significant amount of electrical power for a given amount of diesel fuel.
-
Reliability: Diesel generators are highly reliable and can provide a continuous power supply. They are robust and durable, with a long lifespan when properly maintained.
-
Quick Start: Diesel generators can start and reach full operating capacity quickly, making them suitable for emergency power backup applications.
-
High Power Output: Diesel generators are capable of providing a high power output, making them suitable for applications where a substantial amount of electricity is required.
-
Fuel Availability: Diesel fuel is widely available in most parts of the world, making it a convenient choice for power generation.
-
Low Maintenance: Diesel engines generally require lower maintenance compared to other types of engines, which reduces operational costs.
-
Steady Voltage and Frequency: Diesel generators can maintain a stable output voltage and frequency, which is crucial for sensitive electronic equipment and machinery.
-
Wide Range of Applications: Diesel generator sets are versatile and can be used in a wide range of applications, including residential, commercial, industrial, and remote locations.
-
Remote Operation: They can be operated remotely and are suitable for off-grid or remote locations where access to the electrical grid is limited.
-
High Torque: Diesel engines provide high torque at low RPM, making them suitable for heavy-load applications and industries.
-
Longevity: When properly maintained, diesel generator sets have a long operational life, providing reliable power for many years.
-
Load Handling: Diesel generators can handle varying load demands efficiently, making them adaptable to dynamic power needs.
WORKING PRINCIPLE
The working principle of a diesel generator set is as follows:
Combustion Process: Diesel fuel is injected into the engine's cylinders. As the piston compresses the air in the cylinder, the diesel fuel is atomized and ignites due to the high temperature and pressure, leading to the combustion of the air-fuel mixture.
Power Stroke: The combustion process produces a high-pressure gas that forces the piston downward. This is the power stroke, and it converts the chemical energy of the diesel fuel into mechanical energy.
Crankshaft Rotation: The movement of the piston is transferred to the crankshaft, causing it to rotate. The crankshaft's rotation is what ultimately drives the generator to produce electrical power.
AC Generation: The generator, which is coupled to the crankshaft, consists of coils of wire and a rotor. As the rotor spins, it creates a rotating magnetic field. The interaction between this magnetic field and the coils of wire induces an alternating current (AC) voltage in the stator windings of the generator.
Voltage Regulation: The voltage generated by the generator can be regulated to maintain a stable output voltage within the desired range.
Control System: The control system of the diesel generator set monitors parameters like voltage, frequency, and engine temperature. It also handles the automatic start-up and shutdown of the generator in response to power demand or power loss.
Output of Electrical Energy: The generated AC power can be used to supply electrical energy to various loads, which could be residential, industrial, or commercial.
Diesel generator sets are commonly used as backup power sources in case of electrical grid failures or where a stable and independent power source is needed. Their working principle involves the conversion of chemical energy from diesel fuel into mechanical energy, and then further into electrical energy to provide power for various applications.